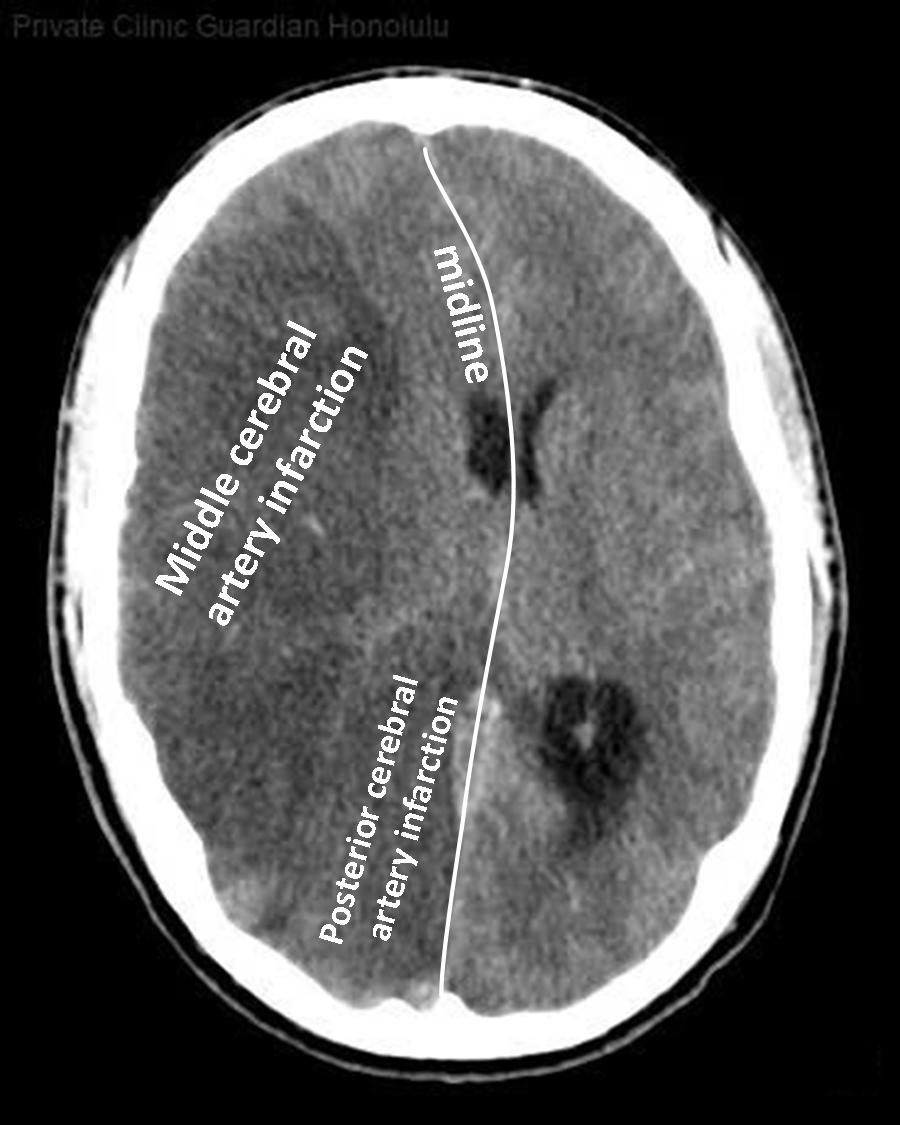
In the layers 4 to 39 on the right side (note R = right) of this computed tomography (CCT) without contrast agent there is an extensive infarct in the territory of the middle and posterior cerebral artery. An ischemic stroke is caused by the occlusion of one or more blood vessels in the brain. Brain ischemia is then a condition in which there is insufficient blood flow to the brain to meet metabolic demand consequently associated with neurological deficits. Here the midline is clearly shifted to the contralateral side. The treatment of choice therefore, in addition to an acute intracranial pressure therapy, is an immediate, large osteoclastic trepanation to give room for the cramped brain.

© Wolfgang Schramm (2008)
• Homepage
• Zu deutscher Sprache wechseln